CBD oil (or Cannabidiol) is the new popular treatment for several health issues and concerns, including chronic skin conditions.
Research on its calming, anti-inflammatory effects continues to grow as CBD oil-infused lotions, salves and more are on the market and being used by consumers. CBD oil may be beneficial for those who suffer from skin conditions like acne, eczema, and psoriasis.
CBD and the Endocannabinoid System
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is one of our body’s built-in regulatory systems with a primary goal of homeostasis. It was named after scientists discovered the interaction our bodies have with compounds from the cannabis plant.
But the entire system actually functions without ever coming into contact with any cannabis. The ECS is made up of neurotransmitters, receptors, and enzymes that help break down both endocannabinoids (from the body) and phytocannabinoids (from plants).
Cannabinoid receptors were found in 1988 in the brain of a rat. Researchers discovered that these receptors were present in humans as well. Throughout the years, research has shown that the endocannabinoid system helps to regulate important functions of the body such as:
- Appetite
- Immune function
- Motor control
- Inflammation
- Mood
- Pain

In the endocannabinoid system, there are two major types of receptors. CB1 receptors are located mostly in the central nervous system, while CB2 receptors are located mostly in the immune system, related organs, and peripheral tissue — including skin.
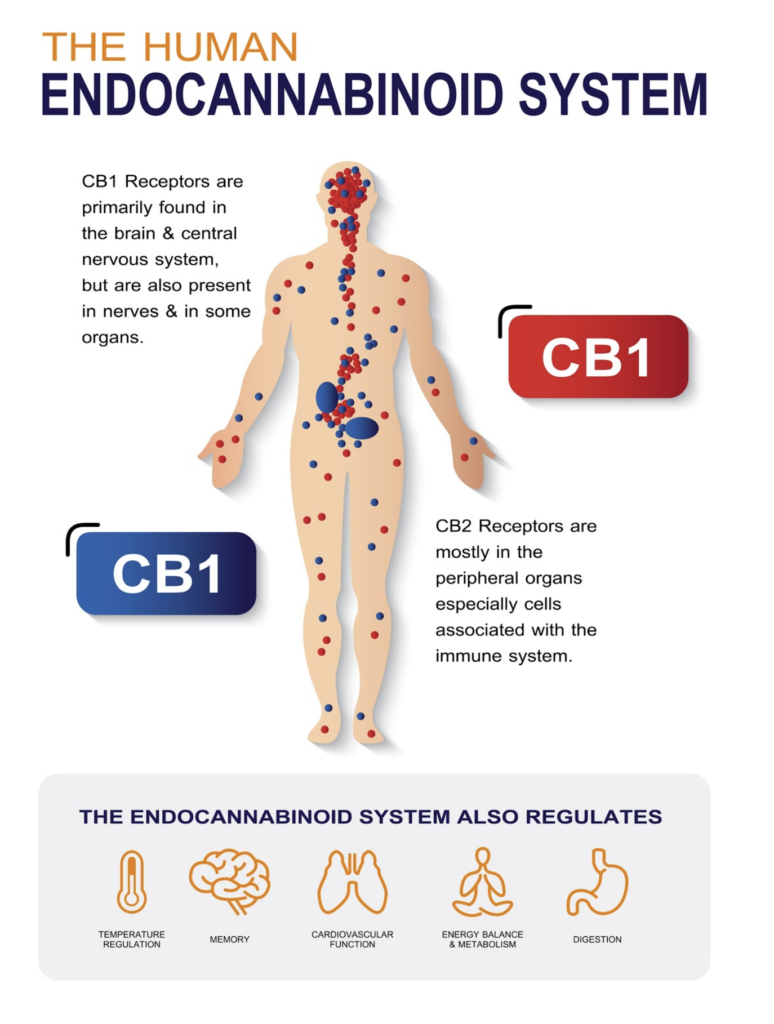
It seems as though our skin is primed and ready to receive the benefits CBD has to offer. This concentrated liquid extracted from the cannabis plant has become well known to consumers and is now present in the world of skincare. We examine the effects of CBD oil on three serious skin conditions.
CBD Oil for Acne
One of the health benefits of CBD oil is that it can be a skin care treatment for acne, the most common skin condition in the United States.
Acne is caused by the buildup of oil and dead skin cells in hair follicles. This buildup causes the skin to become inflamed and the excessive production of sebum, an oily substance secreted by the sebaceous glands. This type of environment on the skin can encourage bacterial growth, leading to breakouts and pimples.
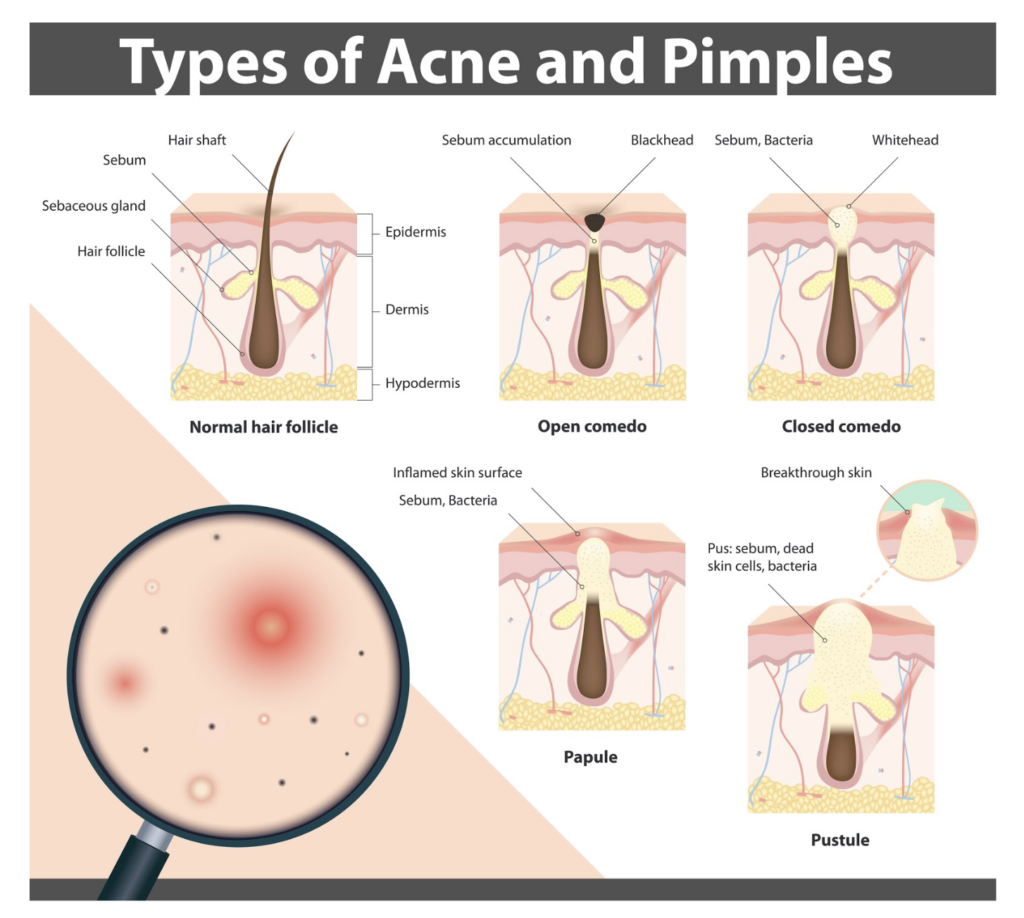
CBD oil is an effective acne treatment because it’s powerfully anti-inflammatory. CBD oil triggers anti-inflammatory properties and prevents excess amounts of sebum from being created, preventing breakouts and blemishes. CBD skin care may also be beneficial to those who experience chronic pain due to acne.
Initial results from scientific studies on CBD oil for acne have proven promising, however more high-quality human trials are needed. CBD skin care products are a cousin to hemp seed oil, or hemp oil, derived from the cannabis sativa plant as well. Both are anti-inflammatory and help in moisturization. It is still unclear if one or the other is more effective on acne.
CBD oil can be applied topically or taken orally. Applying topically can help to treat and target specific breakouts of the skin, while ingesting CBD products can help with the long-term prevention of acne.
When applied topically, CBD oil can be mixed with a carrier oil such as jojoba, safflower, sunflower, castor, argan or rosehip seed oil. In order to avoid side effects, before applying CBD oil directly to the skin, it is important to discuss your condition with a dermatologist, especially if you have sensitive skin. You should also do a “spot test” to ensure you don’t have an allergy to CBD oil, although this is rare.
CBD Oil for Eczema
Atopic dermatitis (AD), or eczema, is a condition that causes inflamed, red, and itchy skin. Eczema can occur at any age and is common in adults and children. Eczema is chronic and has no cure. Dry skin, itchy skin, red or irritated patches, and scaly or cracked skin are some symptoms of eczema.
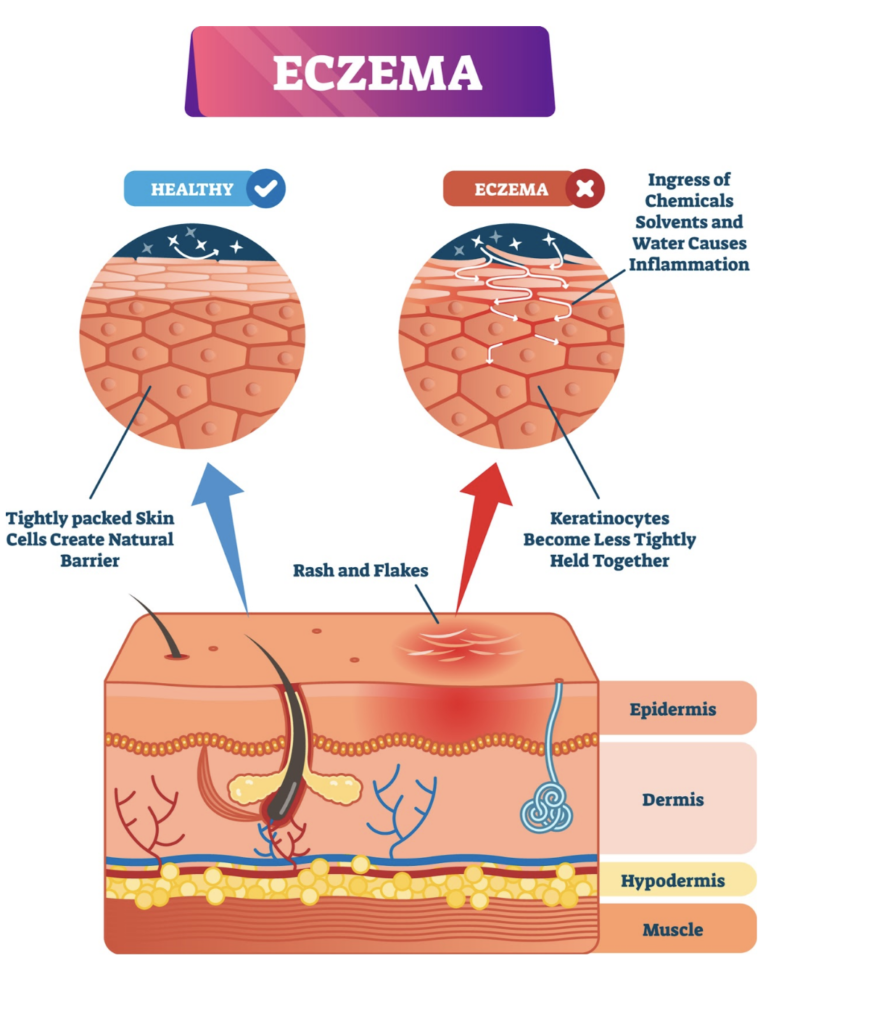
CBD products may prove to be helpful in relief of eczema symptoms. We already know that cannabidiol has anti-inflammatory properties. CBD oil also has antimicrobial and anti-itch qualities that contribute to the treatment of eczema. When flare-ups occur on the skin, CBD products can be applied to reduce both the symptoms and appearance of AD.
According to the Handbook of Cannabis and Related Pathologies, the cannabinoid receptors and cannabinoids in the endocannabinoid system aid in the treatment against contact allergic inflammation. This means that topical CBD may be able to contribute to dermatology and treat inflammatory skin diseases such as eczema and allergic contact dermatitis.
When purchasing everyday CBD oil products, specifically for skin diseases like AD, caution should be taken to avoid irritants that may be present in products like creams and salves. Topical CBD oil products for eczema include body butters and moisturizing skin lotions.
Consumers will want to be sure to purchase high quality CBD skin care product from reputable sources. The FDA has yet to approve non-synthetic cannabinoid-based topical therapy for medical skin conditions like eczema. Research is still ongoing in this area, so talking to a doctor about topical CBD is important.
CBD Oil for Psoriasis
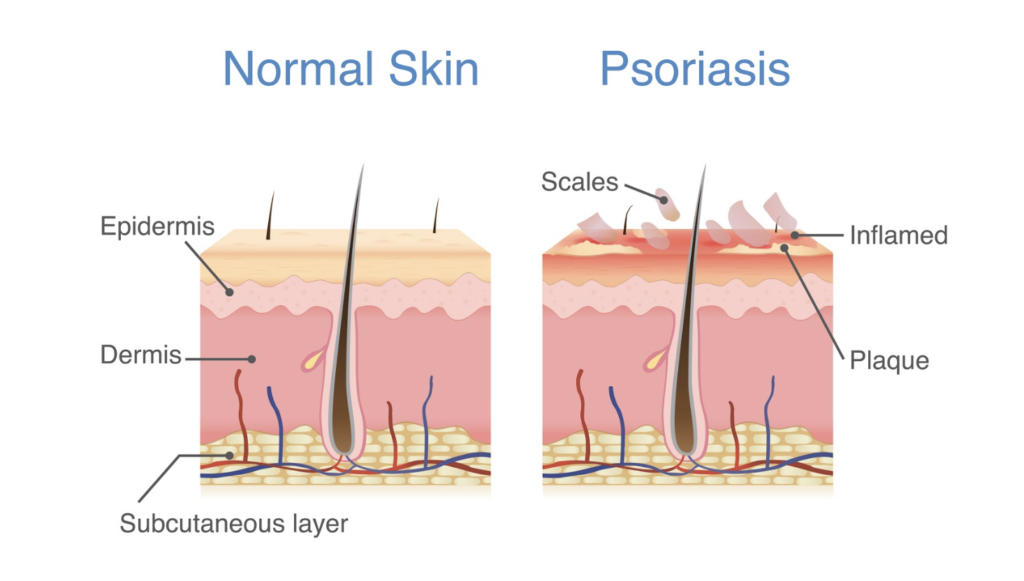
Using CBD could serve as an effective treatment for psoriasis as well. Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disorder, meaning that the immune system impacts healthy cells in the body. This skin condition causes skin cells to be produced at a rapid rate, reaching the surface of the skin before they are able to mature.
The rapid skin cell growth causes skin to be scaly. Other symptoms of psoriasis include redness, swelling, and discomfort. Those with skin diseases like psoriasis may develop psoriatic arthritis, which causes swelling and stiffness of the joints and can be very painful.
According to the National Psoriasis Foundation, there are several psoriasis treatments such as biologic drugs, oral treatments, phototherapy, and topicals.
One particular 2013 study suggested that cannabis and cannabinoid receptors may treat psoriasis by slowing the rapid growth of keratinocytes, stating “cannabimimetic agents might be relevant for the treatment of several skin conditions… such as psoriasis and wound healing.” Keratinocytes are the cells produced immaturely in psoriasis patients.
Another way that CBD products can treat symptoms of psoriasis is through the treatment of chronic pain. When individuals experience psoriasis flare-ups, CBD may be helpful in soothing the pain caused by the skin condition.
An article from the British Pharmacological Society states that cannabinoids are safe and effective in neuropathic pain, with evidence regarding fibromyalgia and rheumatoid arthritis. Stress is another symptom of psoriasis that can be treated with CBD oil, as its calming effects have been known to help soothe anxiety.
Topical CBD oil skin care products are ideal for psoriasis treatment. Topical creams can have a cooling effect that helps to relieve itchiness and discomfort.
In Summary
- The endocannabinoid system is a built in biological system that interacts with the cannabis plants. This system can regulate important functions of the body and interacts with cannabidiol.
- CBD is a compound that can treat many skin conditions such as acne, eczema, and psoriasis.
- CBD treats acne by decreasing the amount of buildup or sebum in the body. Topical use of CBD may be able to prevent long term acne of the skin.
- Eczema can be treated by CBD through its anti-inflammatory and anti-microbial properties.
- The chronic autoimmune disorder, psoriasis, may also see improvement when treated with CBD. Studies suggest that CBD slows the rapid production of immature skin cells caused by the disorder.
Sources
- Pertwee, R. G. (2006). Cannabinoid pharmacology: the first 66 years. British journal of pharmacology, 147(S1), S163-S171. : https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1760722/
- El Manira, A., & Kyriakatos, A. (2010). The role of endocannabinoid signaling in motor control. Physiology, 25(4), 230-238. : https://www.physiology.org/doi/full/10.1152/physiol.00007.2010
- Ashton, C. H., & Moore, P. B. (2011). Endocannabinoid system dysfunction in mood and related disorders. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica, 124(4), 250-261. : https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1600-0447.2011.01687.x
- Fine, P. G., & Rosenfeld, M. J. (2013). The endocannabinoid system, cannabinoids, and pain. Rambam Maimonides medical journal, 4(4). Full Text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3820295/
- Pertwee, R. G. (1997). Pharmacology of cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 receptors. Pharmacology & therapeutics, 74(2), 129-180. Abstract: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9336020
- Ständer, S., Schmelz, M., Metze, D., Luger, T., & Rukwied, R. (2005). Distribution of cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1) and 2 (CB2) on sensory nerve fibers and adnexal structures in human skin. Journal of dermatological science, 38(3), 177-188. Abstract: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15927811
- Fine, P. G., & Rosenfeld, M. J. (2013). The endocannabinoid system, cannabinoids, and pain. Rambam Maimonides medical journal, 4(4).: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4151231/
- Bíró, T., Tóth, B. I., Haskó, G., Paus, R., & Pacher, P. (2009). The endocannabinoid system of the skin in health and disease: novel perspectives and therapeutic opportunities. Trends in pharmacological sciences, 30(8), 411-420.: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2757311/
- Ali, E. M., Almagboul, A. Z., Khogali, S. M., & Gergeir, U. M. (2012). Antimicrobial Activity of Cannabis sativa L. Chinese Medicine, 3(01), 61.: https://www.calgarycmmc.com/Antimicrobial-Activity-of-Cannabis-sativa-L.pdf
- Tüting, T., & Gaffal, E. (2017). Regulatory Role of Cannabinoids for Skin Barrier Functions and Cutaneous Inflammation. In Handbook of Cannabis and Related Pathologies (pp. 543-549). Academic Press.: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780128007563000673
- Klein, T. W. (2005). Cannabinoid-based drugs as anti-inflammatory therapeutics. Nature Reviews Immunology, 5(5), 400.: https://www.nature.com/articles/nri1602
- Ramot, Y., Sugawara, K., Zákány, N., Toth, B. I., Bíró, T., & Paus, R. (2013). A novel control of human keratin expression: cannabinoid receptor 1-mediated signaling down-regulates the expression of keratins K6 and K16 in human keratinocytes in vitro and in situ. PeerJ, 1, e40. Full Text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3628749/
- Lynch, M. E., & Campbell, F. (2011). Cannabinoids for treatment of chronic non‐cancer pain; a systematic review of randomized trials. British journal of clinical pharmacology, 72(5), 735-744.: https://bpspubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/j.1365-2125.2011.03970.x

