CBD for skin care is a hot topic in dermatology. CBD oil and hemp oil have only recently gained large traction in the minds of the public. Millions of Americans claim their calming effects help with anxiety and pain relief — but what can these compounds do for skin?
Daily, people add it to their coffee, post-work smoothies, and even face creams for a healthy skin care routine. With its many touted health benefits, it seems CBD has taken the world by storm and is now making its way into skin care and beauty products. We take an honest look at research to find CBD’s proven benefits for skin.
What is CBD?
CBD is a compound that comes from the hemp plant. CBD, which is short for cannabidiol, is used in many products on the market, due to its multiple health benefits.
CBD is a naturally occurring substance that is safe and non-addictive.
It is now a popular natural remedy used for many health issues. CBD oil is made from extracting CBD from the leaves of a cannabis plant, then diluted with carrier oils such as hemp seed oil or coconut oil.
Backed by scientific evidence, CBD has been known to relieve pain, especially associated with diseases like multiple sclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis due to its anti-inflammatory properties.
CBD is helpful in treating anxiety and depression as well as alleviating cancer-related symptoms and benefiting heart health.
There are some side effects of CBD, including nausea, irritability, and fatigue. (1)
Though there have been disputes over its legality, CBD derived from hemp is legal in all 50 states as long as it adheres to a few regulations. Such as:
- The hemp must contain less than 0.3% THC
- The hemp must adhere to the shared state-federal regulations
- The hemp must be grown by a properly licensed grower
Definitely check with your employer before introducing CBD into your routine. There are many misunderstandings surrounding these products.
Does CBD have THC?
So, what’s the deal with marijuana and hemp? The plant, Cannabis sativa’s, primary species are hemp and marijuana. Both of these species contain CBD, but hemp contains a higher percentage of CBD.

There are no levels of THC, or tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), in CBD.
THC is a psychoactive, meaning you experience euphoria or sedation when taking it and is the typical experience you think of when you think of marijuana.
However, both CBD and THC have therapeutic attributes.
Actually, CBD and THC are only two of several different compounds within the cannabis plant that can have medicinal benefits (see chart below for a few others).

When purchasing CBD, it is important to remember to buy third-party-tested CBD. The FDA does not regulate this supplement and therefore, CBD could contain small amounts of THC.
According to Harvard Medical School, “You cannot know for sure that the product you buy has active ingredients at the dose listed on the label. In addition, the product may contain other (unknown) elements. We also don’t know the most effective therapeutic dose of CBD for any particular medical condition.” (2)
How to Take CBD
CBD can be taken in a variety of ways. First, it may be swallowed. CBD can be swallowed in the form of CBD oil, tinctures, edibles, capsules, or powder. Once CBD is ingested, it passes through the digestive tract before making its way through the bloodstream.
CBD can also be taken orally under the tongue or inhaled. I do not recommend the inhaled method. Ingesting under the tongue allows CBD to enter the bloodstream through the blood vessels in the mouth, resulting in full-body effects. This way, it takes about 30 minutes before effects are experienced.
One way for CBD to treat the skin is if it is applied topically. Applying CBD directly to the skin is helpful in on-the-spot treatment. When applied topically, the hemp-derived nutrients are immediately absorbed through the skin. For long term results, oral usage of CBD products paired with topical skin care products may be best.
The Endocannabinoid System
Do you know that we have an entire system in our body that was discovered because of cannabis? It’s called the endocannabinoid system, and it’s named so because cannabinoids were the first compounds discovered that interacted with this system. (3)
The endocannabinoid system is involved in appetite signaling, stress coping mechanisms, and pain relief. The purpose of this system is homeostasis — or returning to a stable normalized state.
In reference to CBD, there are two major types of cannabinoid receptors in the body: Type 1 Cannabinoid receptors (CB1) and Type 2 Cannabinoid receptors (CB2).
CB1 receptors are mostly located in the nervous and musculoskeletal system as well as some organs and tissues. CB2 receptors are in the immune system, skin and other tissues (see figure below). There are some overlaps as well where you will find both receptors in the same organ system or tissues.
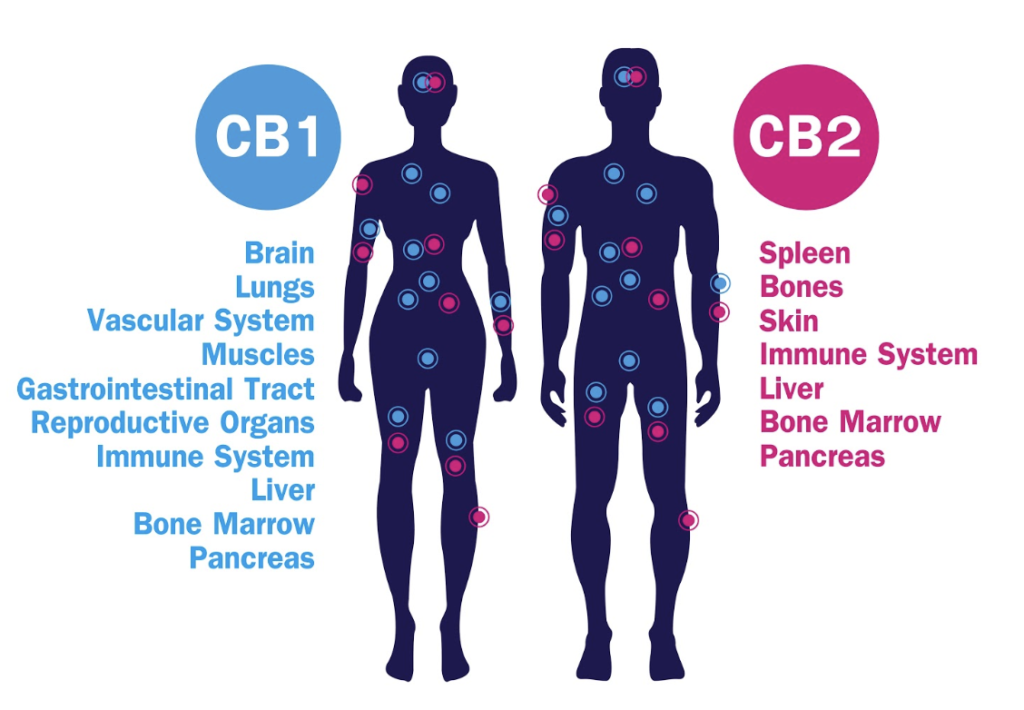
With the external and internal benefits of CBD listed here, our bodies have a built in system ready to take action.
Benefits of CBD in Skin Care: Anti-Inflammatory
CBD oil has been known to serve as an anti-inflammatory. CBD is relaxing and it relieves pain when taken internally, but it has also been shown to help to reduce the pain that inflammatory skin conditions cause.
Anti-inflammatory properties help relieve aggravated skin. While inflammation is a common skin issue that many people deal with, CBD can be an effective treatment for some very specific ailments. Acne prone skin, sunburn, and even post-surgical procedure skin can reap the benefits.
For acne prone skin, applying CBD topically can help reduce breakouts and redness. Studies have shown that CBD can help to lower level of sebum in the skin. Sebum is an oily or waxy substance produced by the skin can lead to acne. CBD helps regulate oil production, which in turn reduces acne. (4, 3)
While cannabinoids exhibit anti-inflammatory properties, research suggests that it has pro-inflammatory and anti-tumor properties as well.
A study review published in December 2018 looked at databases reporting on cannabinoids in relation to skin cancer, acne, allergic contact dermatitis, and more. They acknowledge the efficacy of many treatments, but urge for further research in all areas. (5)
Benefits of CBD in Skin Care: Antioxidant and Soothing Properties
CBD contains essential nutrients needed to encourage skin health. Vitamins, minerals, and proteins, such as vitamins A and D, help to repair the skin, support skin cell growth and keep skin soft.
In CBD, vitamin C and E are powerful antioxidants that protect the skin’s collagen from sun damage. Antioxidants can help to counteract signs of aging caused by free radicals. CBD oil applied topically can help to lessen visible signs of aging skin. (6)
There are CBD anti-aging creams that may be able to help reduce the appearance of skin issues such as dullness and wrinkles. The skin-calming effects of CBD can help to ease sensitive skin, dry skin, and conditions like psoriasis and eczema. Additionally, nutrients like vitamin E can help to improve skin quality and protection. (7, 8)
What Kind of CBD Skin Care Products Should I Take?
The CBD industry is still fairly young, and doing your research is important when purchasing CBD beauty products. Also, be mindful that CBD may interact with some of your medications.
Finding high quality, pure CBD oil can get pretty expensive. Products that claim to be “full spectrum” may contain THC, however they must contain less than 0.3% of THC to be legally sold in all 50 states. Don’t worry, you should not experience a high from full spectrum CBD products.
In broad spectrum CBD products, THC has been removed during the extraction process. CBD isolates are a form of pure CBD and has no THC.
You may need to test for the best CBD product for your skin condition or skin type. There are CBD eye creams, lip balms, body lotions. For systemic results, It’s best to start by taking CBD oil under your tongue to test for side effects.
Here are a few high quality CBD product brands that I’ve used myself as well as my patients to get you started on some product brand options as you explore what is the best one for you.
- Gone Green Hemp
- Endorsed by Kevin Harrington from Shark Tank and recognized for its efficacy
- Full-spectrum high-grade organically grown hemp oils (less than 0.3%THC)
- Unique CBD infused nut butters to get your healthy fats (Great for those on keto!)
- World’s first Organic Coconut Cream with High Cannabinoid Hemp Oil Extract!
- Upgrade your coconut oil with “Gone Green’s CBD Coconut oil”
- Topical CBD salve
- Order directly online https://gonegreenhemp.com/
- ProVerde laboratory accreditation
- Kannaway
- Kannaway’s CBD hemp oil is sourced from hemp grown in Northern Europe free of pesticides, herbicides, or chemical fertilizers
- Wide variety of product options including CBD infused coffee, gum, tea, pet chews, topical salve, hemp clothing etc.
- My favorite is their skin care product line called “Cannabis Beauty Defined” that contains a proprietary blend of natural botanical ingredients, including goji berry, dragons blood, rose hips, poria cocos, astragalus root, and more, all working synergistically to enhance your natural glow and hydrate your skin
- Membership model of purchasing product
- ProVerde laboratory accreditation
- Ultracell by Zillis
- Ultracell products have been formulated to have 94% absorption rate and up to 12 hour bioavailability
- There is a wide array of CBD products including: Ultra Cell flavored (Lemon or Berry), Ultra Raw natural and unsweetened, Ultra Edge for Cognitive support, Ultra Dream for sleep, Ultra Ice for homeostasis support, Ultra Burn for weight management, Topical CBD salve
- Membership model of purchasing product
In Summary
- CBD, derived from the hemp plant is used to combat many health issues including, but not limited to, anxiety, chronic pain, acne, and skin issues.
- There can be very low to zero levels of THC in CBD essential oils, making it non-psychoactive and safe for everyday use.
- CBD can be taken under the tongue, swallowed or applied topically.
- The anti-inflammatory properties in CBD help to prevent acne, redness, and other skin disorders. Antioxidants also soothe and soften the skin.
Sources
- Shannon, S., Lewis, N., Lee, H., & Hughes, S. (2019). Cannabidiol in Anxiety and Sleep: A Large Case Series. The Permanente journal, 23. Abstract: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30624194
- Sawler, J., Stout, J. M., Gardner, K. M., Hudson, D., Vidmar, J., Butler, L., … & Myles, S. (2015). The genetic structure of marijuana and hemp. PloS one, 10(8), e0133292. Full text: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0133292&
- Zou, S., & Kumar, U. (2018). Cannabinoid receptors and the endocannabinoid system: signaling and function in the central nervous system. International journal of molecular sciences, 19(3), 833. Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5877694/
- Oláh, A., Tóth, B. I., Borbíró, I., Sugawara, K., Szöllõsi, A. G., Czifra, G., … & Ludovici, M. (2014). Cannabidiol exerts sebostatic and antiinflammatory effects on human sebocytes. The Journal of clinical investigation, 124(9), 3713-3724. Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4151231/
- Marks, D. H., & Friedman, A. (2018). The Therapeutic Potential of Cannabinoids in Dermatology. Skin Ther. Lett, 23, 1-5. Abstract: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30517778
- Hampson, A. J., Grimaldi, M., Axelrod, J., & Wink, D. (1998). Cannabidiol and (−) Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol are neuroprotective antioxidants. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 95(14), 8268-8273. Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC20965/
- Bíró, T., Tóth, B. I., Haskó, G., Paus, R., & Pacher, P. (2009). The endocannabinoid system of the skin in health and disease: novel perspectives and therapeutic opportunities. Trends in pharmacological sciences, 30(8), 411-420. Abstract: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19608284
- Poljšak, B., & Dahmane, R. (2012). Free radicals and extrinsic skin aging. Dermatology research and practice, 2012. Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3299230/
