Almost daily, I’m asked by patients in my clinic if there are any natural supplements they can take to address their hormonal breakouts, weight gain, and overall health. While these conditions are unfortunate, there’s good news: a DIM supplement can help.
Because of its estrogen-balancing benefits, DIM is often used for:
- Hormonal acne
- PCOS
- Endometriosis
- Weight loss
- Fitness
- Cancer prevention
Once you’ve addressed the basics of diet, lifestyle, and toxin exposure, it’s time to consider the impact of hormone balance on your health.
As a proponent of holistic dermatology, I believe in treating skin and body issues from the inside out — that’s why I recommend a DIM supplement.
This nutrient, found naturally in foods you’re already eating, addresses far more than just some cosmetic concerns. In my years of practice, and seeking holistic care for my own health concerns, I’ve learned that natural solutions like a DIM supplement can heal from the inside out.
What is DIM (diindolylmethane)?
What is DIM? Diindolylmethane (DIM) is a natural phytonutrient that can be found in cruciferous vegetables. These types of veggies include:
- Broccoli
- Cauliflower
- Cabbage
- Kale
- Collards
- Radishes
- Brussels sprouts
- Mustard greens
- Watercress
- Turnips
In these vegetables, DIM is found in a form called Indole-3-Carbinol (I3C). As our digestive system breaks down these cruciferous vegetables, it joins together two I3C molecules to make DIM. The phytochemical DIM is basically two I3C molecules joined into one larger molecule.

I’m usually asked at this point: just how much broccoli does a patient have to eat to get enough DIM to help their breakouts? Realistically, you would have to eat two pounds to get about 20-30 milligrams of DIM — and that’s not even close to enough.
Typically, a starting dose is 100mg of DIM daily and some patients increase to twice daily. That would be 8 and 16 pounds of broccoli!
I like eating my vegetables, but obviously, we can’t keep up truckloads of broccoli per day. Thankfully, DIM comes in dietary supplement form.
How does DIM work?
A supplement that can help with so many hormonal imbalances may sound too good to be true.
Does DIM really work?
Yes, DIM works to treat many issues, including:
- Acne treatment
- Detoxification balancing estrogen levels
- Weight loss
- Cancer prevention

How exactly does DIM work, and what makes it so effective in so many different health problems?
The health benefits of DIM primarily stem from how it helps your body to process estrogen. For many of the problems outlined in this article, estrogen dominance is the cause.
What is estrogen dominance?
Estrogen dominance refers to a state when your body has more estrogen than it needs, or it’s out of balance compared to your other hormones. It can also occur when too much of the wrong kind of estrogen is in excess.
Estrogen dominance has many different root causes, but is most frequently linked to:
- Excess fat
- Environmental toxins
- Adrenal issues
- Stress
- Immune issues
- Poor digestion
A healthcare provider may be able to help you identify what’s throwing off your estrogen levels.
Now that we know how imbalanced our hormones can be, how do you know if you’re struggling with estrogen dominance? Symptoms may include:
- Acne breakouts
- Irregular or heavy periods
- Water retention, bloating
- Headaches
- Breast swelling and tenderness
- Fibrocystic breast changes
- Weight gain, especially around hips, buttocks, and thighs
- Premenstrual Syndrome (PMS)
- Mood swings/irritability
- Decreased libido
- Thyroid dysfunction
- Fatigue
- Hair loss
If one or more of these symptoms apply to you, you may be struggling with estrogen dominance. Thankfully, a DIM supplement may be able to help.
How does DIM work to correct estrogen dominance?
DIM works in 2 main ways to help your body better balance your estrogen: It can work to help improve the ratio of your “good” and “bad” estrogens, and it also assists in the conversion of testosterone to estrogen.
“Good” Estrogen vs. “Bad” Estrogen
Estrogen metabolites, or breakdown products of estrogen, have big effects on the body, though our understanding of their role is still growing as we learn more. In fact, there are over 40 of these metabolites.
The two we will focus on here are the “good” estrogen, or 2-hydroxyestrone (2-OHE1), and the “bad” estrogen, 16-alpha-hydroxy-estrone (16-OHE1).
2-OHE1 estrogen can prevent tumors, while 16-OHE1 estrogen may promote tumor growth.
2-OHE1 is also considered the good estrogen because its presence is linked to lower body fat and higher lean muscle, while 16-alpha-hydroxy-estrone (16-OHE1) has been linked to higher breast cancer risk.
Clearly, we want more 2-OHE1 and less of 16-OHE1, and their ratio to each other is highly important. A higher level of 2-OHE1 compared to 16-OHE1 protects your body and promotes many beneficial processes.
So, where does a DIM supplement come into play? DIM helps your liver enzymes convert your estrogen metabolites to more 2-OHE1 and promotes a more desirable estrogen metabolism.
As your estrogen ratio moves toward favorable levels, your body benefits. However, unlike synthetic hormones and some less natural treatments, it does not replace, mimic, or produce more estrogen.
DIM and Testosterone
DIM also benefits us in regards to testosterone. When our bodies are producing larger amounts of testosterone, some of it can be converted into estrogen by the enzyme aromatase. DIM helps to inhibit aromatase, meaning that less testosterone is converted into bad estrogens.
When there is too much estrogen, health issues arise. DIM supplements can help regulate the body’s hormone levels and get you back to your balanced self, with sustainable, long-term effects.
Benefits of DIM Supplements
We are still learning more about the powerful effects of this plant-based nutrient, but here are a few of the science-backed benefits. DIM supplements may:
- Suppress tumor growth
- Aid fat loss
- Reduce hormonal acne
- Balance estrogen levels
- Protect against some cancerous tumors
- Prevent or treat thyroid disorders
How to Use DIM for Hormonal Acne
Breakouts occur for many reasons, from unwashed pillowcases to inflammatory foods. But with hormonal acne breakouts, the trigger is often estrogen dominance.
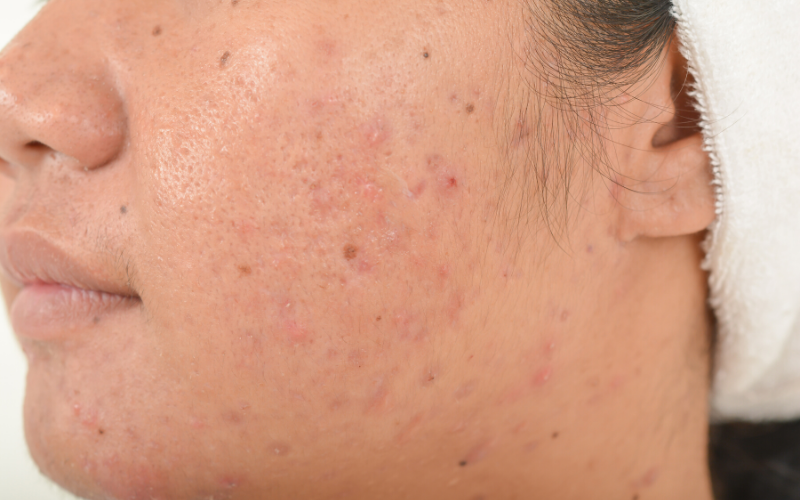
If your acne breakouts are cyclical, red, and cystic, and around the chin and jawline, a hormone imbalance may be the culprit.
Many times, breakouts will be met with harsh prescriptions that carry harmful side effects, instead of solutions that treat the root issue.
Dosage
I start my patients on 100mg once daily of DIM to treat hormonal acne.
Some people may increase that dosage to twice daily after 1-2 months, but check in with your dermatologist before making that decision.
Time To Results
It will take several weeks of taking DIM before you notice a change in your skin. This is because it takes the skin around 28 days to create a new skin layer.
Interestingly, this is also the average number of days of a woman’s menstrual cycle.You will see the greatest improvement after 2-3 months to allow your skin and your hormones a few cycles.
Keep a symptom journal — you may want to observe if DIM also improves any PMS or menstrual cycle symptoms in addition to skin issues!
Effectiveness
DIM supplements are usually very effective for estrogen dominance, as DIM can help regulate your estrogen levels. However, if you have higher levels of testosterone or are testosterone sensitive, DIM can actually worsen your acne.
If you notice after taking DIM that your acne becomes more cystic and you break out more, stop DIM and discuss with your dermatologist other ways to address your hormonal acne.
Our hormones tend to fluctuate depending on other hormones, nutrition, stress, exercise, emotions, etc. Your balance of estrogen, progesterone, testosterone, and cortisol are some of the key hormones that are related to pimple problems, but DIM is not effective for imbalances in all of these.
How to Use DIM for Bodybuilding & Fitness
Bodybuilding and fitness buffs are often faced with too much testosterone in their systems. Unfortunately, this excess testosterone can often convert to estrogen, due to the aromatase enzyme mentioned above.
When this is unchecked, estrogen dominance can happen. Thankfully, DIM can help balance out hormone levels and leave more testosterone available to bodybuilding and fitness enthusiasts.
Dosage
Because bodybuilders tend to have more testosterone floating around, and more potential for unchecked estrogen, a potential starting dose for men is between 200-250mg and 150-200mg for women.
Time To Results
This one isn’t immediately obvious, as the results on DIM for bodybuilding and fitness are more preventative than apparent. However, DIM is able to start balancing estrogen in roughly 30 days.
Effectiveness
For those taking slightly too much testosterone, a DIM supplement to prevent the excess testosterone from becoming an estrogen dominance can be highly effective.
While genetics determine part of how estrogen is processed, DIM is likely to help for those whose hormone levels need support.
How to Use DIM for Weight Loss
It’s no secret that hormonal changes can drastically impact our weight, and estrogen certainly helps us pack on the pounds, especially around our hips and buttocks. A DIM supplement can help metabolites and keep your body from packing on fat.
Dosage
Proponents of DIM for fat loss suggest 100mg a day. However, if you are losing weight for medical reasons, consult with your doctor about adding in this supplement.
Time To Results
Each fat loss case is different, due to individual metabolism and genetics. It’s realistic to expect to see results anywhere between 6 weeks and 6 months, depending on what other weight loss measures you are taking.
Effectiveness
It’s also important to pair this with diet and exercise as well — DIM doesn’t burn fat as much as it helps your body metabolize estrogen better. Your lifestyle choices will strongly determine the effectiveness of DIM for weight loss.
DIM for Men’s and Women’s Health
For both men and women, DIM may offer significant anticancer benefits, particularly for cancer strains that attack the reproductive system or are related to hormone issues.
In women, DIM supplementation has been shown to:
- Potentially protect against breast cancer
- Combat thyroid disease and cancer in women
- Work against breast cancer
For men, DIM supplement can lessen the risk of:
Potential Side Effects of DIM Supplements
The potential side effects of DIM supplements can vary from person to person. Thankfully, most of them are relatively minor, especially when compared to the harm excess estrogen can do.
Side effects of DIM supplements may include:
- Brain fog
- Tiredness and fatigue
- Darker urine (yellow or brown)
- Headache
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
Some of these symptoms may stem from the initial balancing act of hormones in the body, while others may indicate you’re taking a higher dose than necessary.
How much DIM supplement should you take?
- For men: 150-200mg, once per day
- For women: 100mg, once per day
Some women need more DIM and can increase the dose to 100mg, twice daily.
However, do not exceed 200mg daily, as some of the more significant side effects are related to doses of 300mg or more.
When in doubt, check with your healthcare provider.
Be sure to start with the lowest dose possible, and only increase after you have taken it for 2-3 months.
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, trying to become pregnant, or have cancer or other hormone sensitive health issues, do not take DIM before you consult your physician.
If you have health issues with your kidneys, you should also not take DIM.
You should also be aware of any potential interactions with your current medications.
Does a DIM supplement make you sleepy? It’s possible for a DIM supplement to make you feel sleepy or fatigued, especially at first, but most people find this effect mild. Estrogen can affect sleep, so don’t be concerned with some changes as your body balances out this hormone.
How to Choose a Quality DIM Supplement
Now that you’ve seen the myriad of benefits that come with this phytonutrient, you’re likely wondering how to choose a quality DIM supplement.

What is the DIM supplement made of? A DIM supplement is made of an extract of the phytonutrient diindolylmethane in capsule form.
Try to choose one made of organic ingredients, or even one with some additional micronutrients added in.
I also love vegetarian, gluten-free capsules to accommodate dietary restrictions and avoid inflammatory substances in your body.
Before starting DIM, whether for acne, bodybuilding, weight loss, or just general signs of estrogen dominance, it’s wise to talk to your doctor or dermatologist. We can help steer you toward our favorite supplements and recommend a dosage from you.
Sources
- Pondugula, S. R., Flannery, P. C., Abbott, K. L., Coleman, E. S., Mani, S., Samuel, T., & Xie, W. (2015). Diindolylmethane, a naturally occurring compound, induces CYP3A4 and MDR1 gene expression by activating human PXR. Toxicology letters, 232(3), 580-589. Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4568078/
- Bradlow, H. L., Sepkovic, D. W., Telang, N. T., & Osborne, M. P. (1999). Multifunctional aspects of the action of indole‐3‐carbinol as an antitumor agent. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 889(1), 204-213. Abstract: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10668495/
- Bradlow, H. L., Michnovicz, J. J., Halper, M., Miller, D. G., Wong, G. Y., & Osborne, M. P. (1994). Long-term responses of women to indole-3-carbinol or a high fiber diet. Cancer Epidemiology and Prevention Biomarkers, 3(7), 591-595. Abstract: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7827590/
- Jin, H., Park, M. H., & Kim, S. M. (2015). 3, 3′-Diindolylmethane potentiates paclitaxel-induced antitumor effects on gastric cancer cells through the Akt/FOXM1 signaling cascade. Oncology reports, 33(4), 2031-2036. Abstract: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25633416/
- Choi, Y., Kim, Y., Park, S., Lee, K. W., & Park, T. (2012). Indole-3-carbinol prevents diet-induced obesity through modulation of multiple genes related to adipogenesis, thermogenesis or inflammation in the visceral adipose tissue of mice. The Journal of nutritional biochemistry, 23(12), 1732-1739. Abstract: https://pubag.nal.usda.gov/catalog/448204
- Rajoria, S., Suriano, R., George, A., Shanmugam, A., Schantz, S. P., Geliebter, J., & Tiwari, R. K. (2011). Estrogen induced metastatic modulators MMP-2 and MMP-9 are targets of 3, 3′-diindolylmethane in thyroid cancer. PloS one, 6(1). Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3022654/
- Krotkiewski, M., Björntorp, P., Sjöström, L., & Smith, U. (1983). Impact of obesity on metabolism in men and women. Importance of regional adipose tissue distribution. The Journal of clinical investigation, 72(3), 1150-1162. Abstract: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6350364/
- Dalessandri, K. M., Firestone, G. L., Fitch, M. D., Bradlow, H. L., & Bjeldanes, L. F. (2004). Pilot study: effect of 3, 3′-diindolylmethane supplements on urinary hormone metabolites in postmenopausal women with a history of early-stage breast cancer. Nutrition and cancer, 50(2), 161-167. Abstract: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15623462/
- Rajoria, S., Suriano, R., Parmar, P. S., Wilson, Y. L., Megwalu, U., Moscatello, A., … & Tiwari, R. K. (2011). 3, 3′-Diindolylmethane modulates estrogen metabolism in patients with thyroid proliferative disease: a pilot study. Thyroid, 21(3), 299-304. Abstract: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21254914/
- Staub, R. E., Onisko, B., & Bjeldanes, L. F. (2006). Fate of 3, 3 ‘-Diindolylmethane in Cultured MCF-7 Human Breast Cancer Cells. Chemical research in toxicology, 19(3), 436-442. Abstract: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16544949/
- Smith, S., Sepkovic, D., Bradlow, H. L., & Auborn, K. J. (2008). 3, 3′-Diindolylmethane and genistein decrease the adverse effects of estrogen in LNCaP and PC-3 prostate cancer cells. The Journal of nutrition, 138(12), 2379-2385. Abstract: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19022961/
Kim, S. M. (2016). Cellular and molecular mechanisms of 3, 3′-diindolylmethane in gastrointestinal cancer. International journal of molecular sciences, 17(7), 1155. Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4964527/

